Brain infections are serious health conditions that can significantly impact a person’s health and quality of life. They can be caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Brain infections can range from mild conditions to life-threatening diseases, so understanding the symptoms, causes, prevention, and treatment options is crucial. This blog will provide tips on how to recognize, prevent, and manage brain infections effectively.
What is a Brain Infection?
A brain infection occurs when harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, enter the brain and cause inflammation or other disruptions to its normal functioning. The infection can be localized to a particular area of the brain or may affect the entire organ. There are several types of brain infections, including meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscesses, and prion diseases.
- Meningitis is the inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
- Encephalitis refers to inflammation of the brain tissue itself.
- Brain Abscess is a localized collection of pus in the brain.
- Prion diseases, though rare, involve proteins that fold abnormally and cause brain damage.
Common Causes of Brain Infections
The causes of brain infections can vary depending on the type of infection. Some common pathogens that cause brain infections include:
- Bacterial Infections: Meningitis and brain abscesses are often caused by bacterial infections, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae.
- Viral Infections: Viruses like the herpes simplex virus (HSV), enteroviruses, and the West Nile virus can cause encephalitis or meningitis.
- Fungal Infections: Fungi such as Cryptococcus or Candida may lead to fungal meningitis, especially in people with weakened immune systems.
- Parasitic Infections: Parasites like Toxoplasma gondii can cause encephalitis, particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
- Prion Diseases: Prions are misfolded proteins that cause neurodegenerative diseases like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
Symptoms of Brain Infections
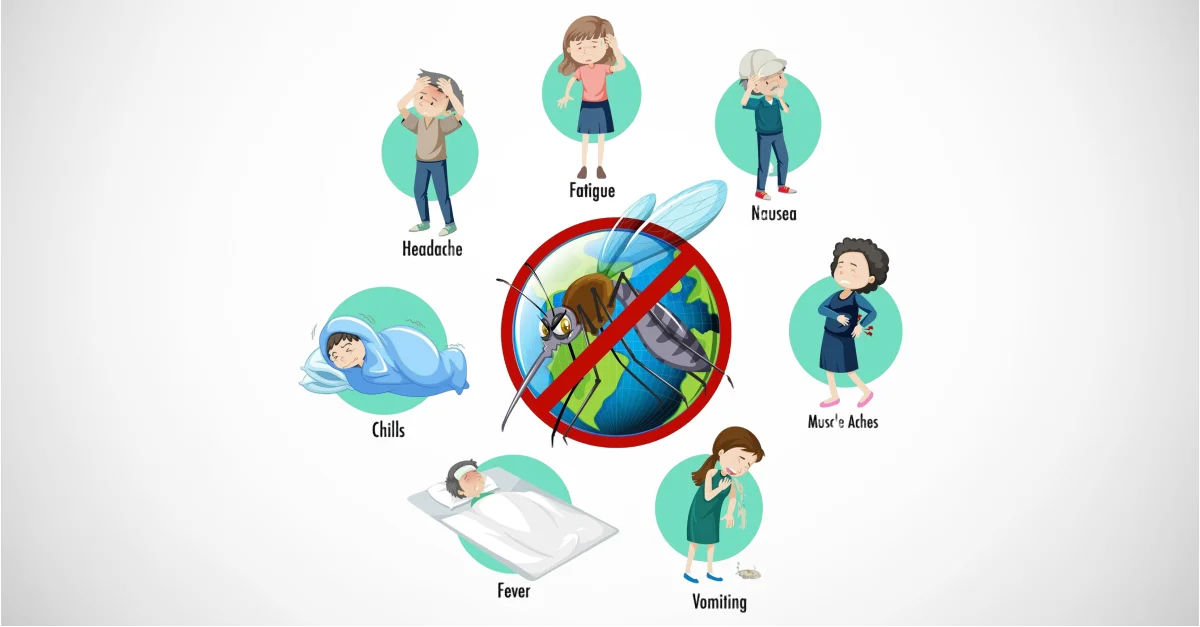
Recognizing the symptoms of a brain infection early is critical for prompt treatment and recovery. Symptoms may vary depending on the type of infection and the severity. Common symptoms include:
- Headache: A persistent or severe headache is often the first symptom of a brain infection.
- Fever: A high fever, often associated with chills, is a common sign of infection.
- Neck Stiffness: Difficulty in moving the neck or pain when trying to tilt the head is a common symptom of meningitis.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms may occur alongside a headache and fever.
- Confusion or Altered Mental State: This includes difficulty thinking clearly, memory problems, or even loss of consciousness in severe cases.
- Seizures: Seizures may occur in cases of encephalitis or brain abscess.
- Sensitivity to Light: Photophobia, or an increased sensitivity to light, is another common symptom in brain infections.
- Fatigue and Muscle Weakness: In some cases, brain infections may cause extreme fatigue, muscle weakness, or paralysis.
Prevention Tips for Brain Infections
Preventing brain infections involves taking measures to reduce the risk of exposure to pathogens. Here are some tips to protect yourself and others:
- Vaccination: Vaccines are one of the most effective ways to prevent certain types of brain infections, such as meningitis. The meningococcal, pneumococcal, and Hib vaccines can significantly reduce the risk of bacterial meningitis. The flu vaccine can help prevent encephalitis caused by the flu virus.
- Good Hygiene Practices: Proper handwashing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals can reduce the risk of infection. Regularly washing hands with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom or handling contaminated surfaces, is key in preventing infections.
- Avoiding Infected: Animals: Rabies, a viral infection, can lead to encephalitis. Avoid contact with animals that may carry the virus, such as bats and stray dogs.
- Safe Travel Practices: When traveling to areas where brain infections are more common (such as regions with high rates of malaria or Zika), take precautions such as using insect repellent, sleeping under mosquito nets, and avoiding unclean water sources.
- Boosting Immunity: Maintaining a strong immune system can help reduce the likelihood of developing severe infections. A healthy diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and managing stress can help strengthen your immunity.
Management and Treatment Tips for Brain Infections
If you suspect that you or someone else may have a brain infection, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can greatly improve the outcome. Here are some treatment tips:
- Antibiotics and Antiviral Medications: Depending on the type of infection, doctors may prescribe antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungal medications to target the specific pathogen. For bacterial meningitis, antibiotics are critical to reducing complications and preventing long-term damage.
- Corticosteroids: In cases of severe inflammation, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce swelling and pressure on the brain.
- Anticonvulsants: If seizures occur, anticonvulsants may be given to control the symptoms and prevent further seizures.
- Hydration and Supportive Care: It’s essential to stay hydrated and rest while undergoing treatment. In some cases, intravenous fluids and electrolyte support may be needed.
- Surgery: In some cases, a brain abscess may require surgical intervention to drain the pus and relieve pressure on the brain.
- Monitoring and Rehabilitation: Patients with severe brain infections may require long-term monitoring and rehabilitation to recover cognitive functions and manage neurological impairments.
Conclusion
Brain infections can be dangerous and even life-threatening, but with the right knowledge and precautions, the risk can be minimized. Recognizing symptoms early, seeking prompt medical treatment, and following preventive measures can significantly reduce the chances of developing a severe brain infection. Make sure to stay informed about vaccinations, hygiene practices, and general health measures to protect yourself and others from these potentially harmful infections. If you experience symptoms such as persistent headaches, fever, or confusion, don’t hesitate to seek medical help to ensure a prompt diagnosis and treatment.