Measles is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the measles virus, primarily spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The virus can spread rapidly in areas with low vaccination rates, affecting up to 90% of non-immune individuals exposed. Symptoms include fever, cough, runny nose, red eyes, and a distinctive rash. Although there is no specific antiviral treatment, severe cases may benefit from vitamin A supplementation to reduce complications. Vaccination remains the most effective preventive measure against measles. Hospitals in Mumbai specialize in measles treatment, focusing on symptom management and minimizing complications. Immediate medical attention is essential for managing the infection, especially in vulnerable populations like young children and those with weakened immune systems.
What is Measles?
Measles is an extremely contagious virus that is caused by the measles virus. It is located in the throat and nose phlegms of people who have been infected. The virus is easily spread through respiratory droplets that are released into the air when a person who is infected coughs, breathes or sniffs. The droplets may remain airborne or settle on the surface for a long time and allow people to get infected after breathing in the contaminated air or touching surfaces that are infected and then touching their nose, eyes or mouth.
Measles is so infectious that if one person suffers from it, as much as 90 percent of the people around them who are not immune be affected as well. People who are infected can spread measles to other people from four days prior up to four days following the rash is visible.
How Does Measles Occur?
Measles is spread primarily by the direct exposure to an affected body’s respiratory fluids. When a person with measles coughs, sneezes or speaks, small droplets that contain the virus are released into the air where they could be inhaled by people. The virus is also able to survive on surfaces for hours and pose a threat to people who come in contact with objects that are contaminated.
How Common is Measles?
- Tourists with measles in a foreign country return to their homes.
- Outbreaks are common in communities with low rates of vaccination.
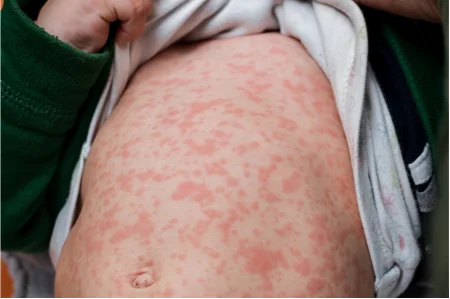
- Rash (usually usually and expanding downwards)
- Cough
- Nose irritated and runny
- Eye irritation (conjunctivitis)
- Fever
Measles is still a widespread illness throughout the world, despite existence of a vaccine that is effective. Based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) measles outbreaks can be found across the globe in all regions. For instance, in the United States, measles cases usually occur during:
In the year 2019 the year that was just beginning, over 1.200 confirmed cases of measles have been confirmed in 31 states. This is the most severe number of incidents since measles became extinct within the U.S. in 2000. In October 2024, 271 cases were reported across thirty states as well as those in the District of Columbia, with more than 80 percent of the cases being non-vaccinated people or those with unconfirmed vaccination status.
Symptoms
The symptoms of measles typically manifest between 10 and 14 days after exposure. Symptoms could be characterized as:
Children who are measles-infected often suffer from severe discomfort and be absent from school because of a loss of appetite and diarrhea and the sensitivity to light. The rash typically appears around fourteen days after exposure. However, those with weak immune systems may not get the rash.
Treatment
There is no particular measles treatment that is antiviral. Medical treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and dealing with issues, like infections caused by bacteria. In the most severe instances, particularly in children hospitalized, vitamin A can be given to lower the risk of complications and speed up the rate of recovery.