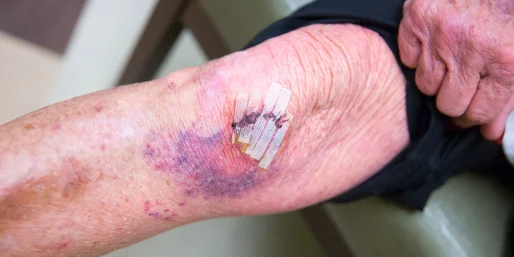
Post Surgical Infections

Post surgical infections, commonly known as surgical site infections (SSIs), occur at or around the area where surgery was performed. These infections can affect the skin, tissues, or even internal organs involved in the surgical procedure. For individuals seeking post surgical infections treatment in Mumbai, addressing both mild surface infections and severe deep tissue complications is crucial to ensuring successful recovery. Despite advances in sterilization and surgical techniques, SSIs remain a frequent complication after surgery. They typically occur when bacteria or pathogens enter the body through the surgical incision, often due to contamination during surgery, improper wound care, or underlying health conditions. Understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and preventative measures is vital to minimize infection risks and support post-operative recovery.
What is a Post-Surgical Infection?
Post surgical infections, often referred to in the field of surgical site infections (SSIs) are infections which occur in the site in which surgery was carried out. The infections can develop within the skin, tissues or organs that are involved in surgical procedures. post surgical infections be anything from minor skin infections to more serious infections that target the internal organs or tissues. They are a typical complications following surgery, and they can hinder recovery and general health if not managed properly.
How Do Post-Surgical Infections Occur?
- Contamination during Operation: Despite efforts to sterilize there are occasions when bacteria get into the surgical area as part of the process.
- Materials or equipment that are contaminated: Tools for surgery or implants that are not sterilized completely can introduce pathogens.
- Inadequate Wound care: Inadequate wound care after surgery could cause an environment for bacteria to flourish.
- The Patient’s Factors: Conditions like obesity, diabetes or a weak immune system make you more susceptible to infections following surgery.
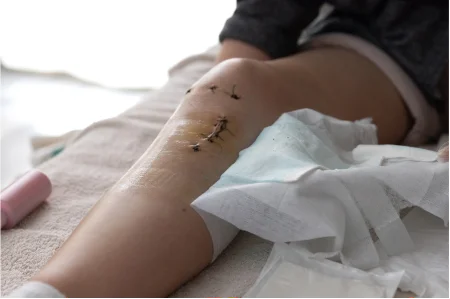
Post surgical infections usually occur when pathogens or bacteria are introduced into the body via the surgical cut. The most common causes are:
How Common Are Post-Surgical Infections?
- Swelling and redness The incision site can turn red, swollen and hot to the touch.
- Tenderness and Pain Pain and tenderness that is greater around the incision, which gets worse with time.
- Pus or discharge Discharge, pus, fluid or any other form of drainage from the site of wound.
- Fever A fever of more than 100.4degF (38degC) could indicate an infection.
- Fatigue Feeling of general malaise or tiredness.
- Delay in Healing The wound could be more difficult to heal that anticipated. In extreme cases the infection could be spread and cause symptoms such as high fever, a rapid heartbeat or confusion. In some cases, it can lead to sepsis which is a life-threatening disease.
- Antibiotics Intravenous or oral antibiotics are usually used to treat infections. The type of antibiotic you choose depends on the bacteria found.
- Wound Treatment The wound might require cleaning and covered frequently to prevent the spread of bacteria. In certain situations the wound could be opened again to drain the affected fluid.
- Techniques to Drain When abscesses or pus develop the use of needles or surgery may be required to eliminate affected fluid.
- Treatment of Pain A painkiller can be prescribed to ease discomfort.
- Hospitalization The most severe cases could necessitate hospitalization for intensive treatment that includes IV antibiotics and constant monitoring. In the case of extreme cases, when an implant or surgical device is involved, further surgical procedures could be required to remove the infected material.
Post surgical infections are among the most frequently encountered complications of surgery. Based on the World Health Organization (WHO) the incidence of surgical site infections is around 2 percent of patients who undergo surgery. Certain kinds of surgery like orthopedic or abdominal surgeries are more susceptible to infections. The likelihood of contracting an infection is also contingent on the duration of surgery and the type of surgery as well as the patient’s overall medical condition.
Symptoms of Post Surgical Infections
The signs and symptoms of post-surgical infections can differ, but the most common symptoms are:
Treatment of Post Surgical Infections
Treatment of post surgical wounds promptly is vital to avoid complications and to ensure a speedy the speed of recovery. Treatment options usually include: